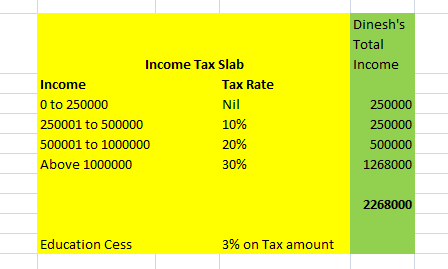
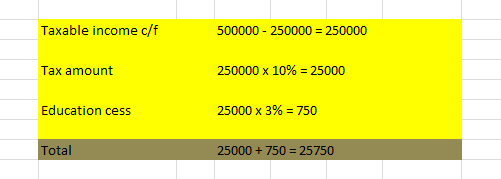
The pay components of gross salary are categorized as recurring and non – recurring pay components.
Read: What is basic salary, gross salary and net salary?
Recurring pay components:
These are master salary components which remain fixed irrespective of performance. Recurring pay components are supposed to occur constantly over a period of time.
Example: Basic salary, House Rent Allowance (HRA), Dearness Allowance (DA) etc.
Non recurring pay components:
Unlike recurring pay components, non recurring pay heads keep changing on monthly basis and are based on performance. An employee may or may not get paid these pay heads constantly throughout the period.
Example: Performance incentive, Bonus, Commission etc.
Components of gross salary:
Basic Salary:
Basic salary is the amount paid to an employee before any extras are added or taken off.
Dearness Allowance (DA):
The Dearness Allowance is a cost of living adjustment allowance paid to government employees, public sector employees and pensioners in India, Bangladesh and Pakistan.
House Rent Allowance (HRA):
House rent allowance (HRA) is a pay component, employees receive from their employer to pay house related expenditure.
Read: House Rent Allowance (HRA) – Meaning and Taxability
Transport Allowance:
Allowance granted to an employee to meet his expenditure for the purpose of commuting between his place of residence and office/place of duty.
Conveyance Allowance:
Allowance granted to meet the expenditure on conveyance in performance of office duty
Medical Reimbursement Allowance:
Fixed component which is received as part of monthly salary. No bills are required to be submitted for taking this allowance.
Leave travel allowance (LTA):
Allowance which is provided to employee to cover travel expenses for vacations.
City Compensatory Allowance:
Allowance which is paid to employees as a compensation for the high cost of living in metropolises and large cities where the standard of living is higher than the national average.
Shift Allowance:
Allowance which is paid when an employees’ working pattern varies from week to week on a rota basis.
Performance Incentives:
Performance incentive is a monetary gift provided to an employee based on performance.
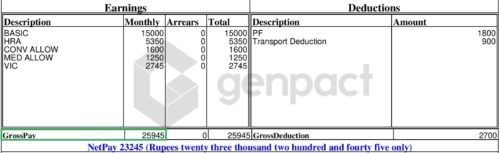
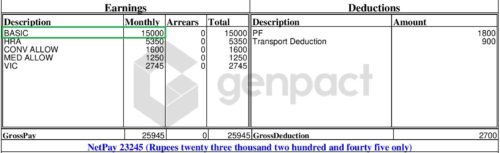
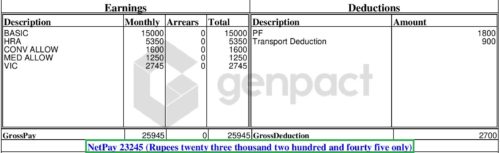
In the above screenshot, the total of all the pay components (Basic salary, HRA, Conveyance allowance, Medical allowance and VIC) is Rs 25,945 which is gross salary.